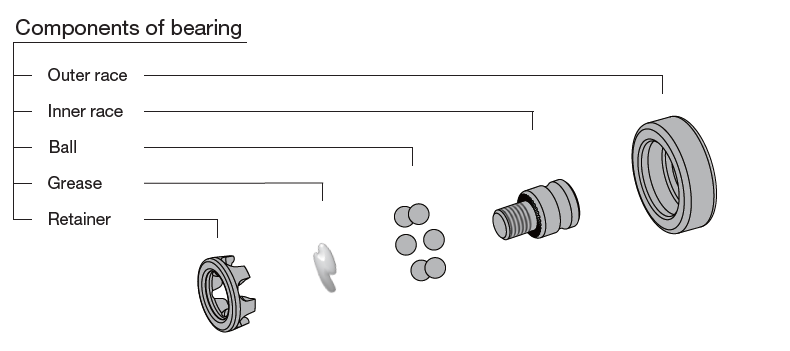
Contents
Relationship between outer race shape and the running surface
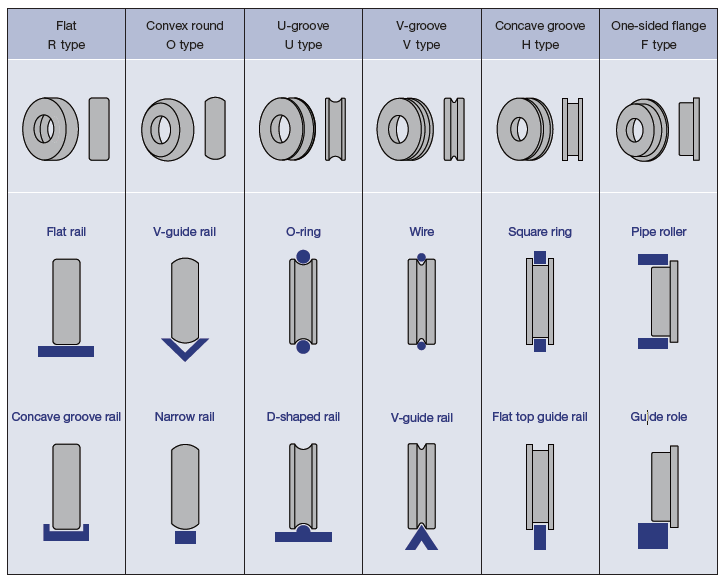
The outer race surface of bearings is typically flat, but TOK offers 6 different outer race shapes, allowing you to choose the most suitable one for your operating environment. The table below summarizes the 6 types of outer race shapes along with examples of compatible running surfaces. Be sure to select the outer race that best matches the shape of the running surface or mating component.
| Flat type | Ideal for use on flat running paths including flat rails or concave groove rail. |
| Convex round type | Ideal for use on flat running paths including V-guide rail or small rails. |
| U-groove type | Ideal for use with O-rings to suppress running noise, or on D-shaped rails. |
| V-groove type | Ideal for use when running a wire along the bearing groove or using on V-guide rails. |
| Concave groove type | Ideal for use with square ring to suppress running noise, or on D-shaped rails. |
| One-sided flange type | Ideal for insertion into both ends of a pipe, or for use as an axial guide. |
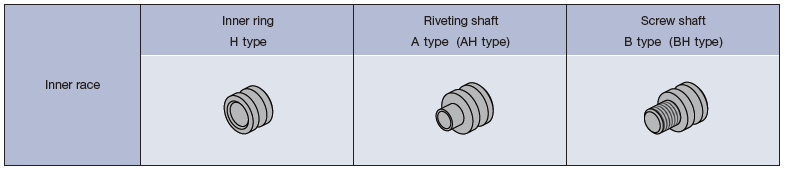
Explanation of inner race shapes and installation methods
The method of installing a bearing varies greatly depending on the shape of the inner race. TOK bearings offer 3 different inner race shapes, each corresponding to a different installation method. While the inner ring type is generally the most common, TOK also provides screw shaft types and riveting shaft types. In particular, the screw shaft type allows for easy installation using a Phillips screwdriver. Each inner race shape is explained in detail, along with videos, so please refer to them and select the inner race most suitable for your application.
How to mount bearing | H type (Inner ring type)
Insert the shaft into the inner ring. Then, to prevent lateral movement, secure the bearing with an E-ring or similar component.
Caution: Make sure the end face of the outer race (the rotating part) does not come into contact with the mating component. Such contact may cause rubbing during rotation and reduce the bearing’s performance.
■Applicable product types
– H type (Inner ring type)
How to mount bearing | A type (Riveting shaft type)
Insert the tip of the riveting shaft into the hole of the mounting component. Next, using the insert (punch) mounted on a spin riveting machine, apply pressure to the tip of the riveting shaft while rotating it. The applied pressure deforms the tip of the riveting shaft, securely joining it to the mounting component. For optimal results, the clearance between the mounting hole shape and the riveting shaft should be minimal. Regarding the thickness of the mounting component, DR-22-A0.5 (with a riveting length of 3.5 mm) is designed for riveting into steel plates with a thickness of 2.3–2.6 mm.
Caution: A backing jig is required to receive the applied pressure. When using it, ensure that the pressure is applied to the opposite end of the riveting shaft and not to the outer race. Applying pressure to the outer race may leave indentations on the balls inside the bearing, which can adversely affect its rotational performance.
■Applicable product types
– A type (Riveting shaft type)
How to mount bearing | B type (Screw shaft type)
Insert the tip of the screw shaft into the screw hole of the mounting component. Next, using a Phillips screwdriver (No. 2 bit), rotate the screw shaft while inserting it to install the bearing. If you are concerned about the cross recessed head, products with a hex socket screw (with “-JH” at the end of the product name), which can be securely tightened with a hex wrench, are also available for consideration.
Caution: We recommend using a No. 2 Phillips bit. Using other sizes, such as No. 1 or No. 3, may result in poor engagement with the screw shaft and could damage the cross recessed head of the screw.
■Applicable product types
– B type (Screw shaft type)
Clearance between bearing and mounting component
When installing a bearing, ensure that the rotating side of the bearing (the outer race side) does not come into contact with the mating component. Typically, clearance washers or similar methods are used to prevent such contact. However, TOK bearings feature a convex outer race surface designed to avoid contact, so there is no need to use washers or other spacers. For riveting shaft or screw shaft type, you can select from 7 different clearance sizes (0.5 mm to 6.0 mm) to suit your application. The inner ring type also offers a wide inner race option, allowing you to select the most suitable bearing for your application environment.
Bearing endurance performance
・Allowable Load and Durability: The allowable load values are based on a total of 1,000,000 rotations.
・Operating temperature range: 0 to 40 °C. *Low-temperature and high-temperature specifications can be designed depending on the application.
・Rotational speed: As a guideline, the allowable load applies up to approximately 300 min⁻¹.
Precautions for use
● Do not use bearings in applications where it may be subjected to impact load. (See Figure 1)
● Ensure that load is applied radially, and avoid axial load. (See Figure 2)
● Improper use of bearings may cause damage or malfunction.
Be sure to understand bearing specifications and usage precautions, and select the most suitable bearing for your application.
Conduct sufficient performance evaluations, durability tests, and environmental tests after mounting bearing to guarantee quality
and safety of your application.
● Do not operate bearing outside its specification or rated value.
Operating bearing outside its specification may cause accident.
● Do not disassemble, modify, rework, or repair bearing.
Decrease in performance or durability may cause failure or accident.
● Do not set fire to the bearing.
Setting fire may cause an accident.

.gif)
-2.gif)
.gif)



700-450-1-336x216.png)
700-450-1-336x216.png)

700-450-1.png)
700-450-1-300x193.png)
